Most 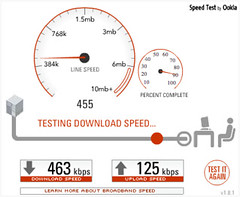 enterprise CTOs are very interested in the “cloud” and ways to tap into cloud-based resources. An interesting aspect of this discussion has been how to access the cloud while on the move. Today’s cellular networks support that access today, and future enhancements are making that support even better and much much faster.
enterprise CTOs are very interested in the “cloud” and ways to tap into cloud-based resources. An interesting aspect of this discussion has been how to access the cloud while on the move. Today’s cellular networks support that access today, and future enhancements are making that support even better and much much faster.
How much faster? I’ll try to put that in context in this post.
Early 3G networks had a download speed of 384kbits per second and an upload speed of 192Kbits per second. The wireless router you might have in your home, by contrast, might have a speed of 54Mbits per second. So, about 140 times faster.
But the 3G networks in place today use new transmission algorithms that enable much faster throughput. Here is a little more context from vendor pages:.
Verizon asserts their broadband access, based on CDMA2000 1x EVDO (Code Division Multiple Access Evolution-Data Only) provides download speeds of up to 1.4Mbits/s and uploads of up to 800kbits/s.
AT&T is leveraging its GPRS technology called EDGE to deliver higher speeds than Verizon’s. AT&T’s EDGE delivers speeds of around 1.7Mbits/s and …
Most  enterprise CTOs are very interested in the “cloud” and ways to tap into cloud-based resources. An interesting aspect of this discussion has been how to access the cloud while on the move. Today’s cellular networks support that access today, and future enhancements are making that support even better and much much faster.
enterprise CTOs are very interested in the “cloud” and ways to tap into cloud-based resources. An interesting aspect of this discussion has been how to access the cloud while on the move. Today’s cellular networks support that access today, and future enhancements are making that support even better and much much faster.
How much faster? I’ll try to put that in context in this post.
Early 3G networks had a download speed of 384kbits per second and an upload speed of 192Kbits per second. The wireless router you might have in your home, by contrast, might have a speed of 54Mbits per second. So, about 140 times faster.
But the 3G networks in place today use new transmission algorithms that enable much faster throughput. Here is a little more context from vendor pages:.
Verizon asserts their broadband access, based on CDMA2000 1x EVDO (Code Division Multiple Access Evolution-Data Only) provides download speeds of up to 1.4Mbits/s and uploads of up to 800kbits/s.
AT&T is leveraging its GPRS technology called EDGE to deliver higher speeds than Verizon’s. AT&T’s EDGE delivers speeds of around 1.7Mbits/s and upload of around 1.2Mbits/s. AT&T also claims that their new protocols (HSDPA/UMTS, for High Speed Downlink Packet Access/Universal Mobile Telephone System) makes it possible to make use of more services and credit this with their ability to let you talk and use the Internet at the same time.
Sprint asserts that its broadband cards delivery 350-500kbps but then say you might get a peak of 3.1Mbps. I wonder if or how often that happens. Sprint also claims that they “lead the way with 4G” and in many ways they seem to be the pioneers here, but they might be defining that term differently than others. Clearly their offering of EVO is revolutionary, it is an incredible device (look for reviews elsewhere on our site). Sprint’s system, which is fast at an advertised .5 to 1.5 Mbps uplink (and peak uplinks at up to 5 Mbps (another source said peak can be 12 Mbps)), is very fast but still no where near the speed I think of when I think 4G.
Really 4G refers to the fourth generation of cellular wireless standards. I consider 4G to be IP-packet-switched networks operating at gigabit speed for access. Most in the field consider WiMAX and LTE (Long term evolution cell) as pre-4G or sometimes 3.5G.
What’s coming next:
A key emerging protocol is HSDPA (High-Speed Downlink Packet Access). HSDPA is sometimes called 3.5G. This protocol is in the HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) family and allows download of up to 14.4Mbits/s download and 5.8Mbits/s upload. Now this is getting interesting.
HSPA+ allows speeds of up to 42Mbits/s. This is almost what you would expect to see in your home wireless LAN. The next step is a project called Long Term Evolution. This LTE will start with providing 150Mbits/s to handheld devices and soon thereafter expect protocols and algorithms to increase that up to 1gig of bits per second to your mobile device.
When will these new protocols and speeds be available to consumers? The answer is, the best roadmaps I have seen are all tightly held insider views, but if you look at what is being rolled out right now we should expect a continuing stream of announcements that brings the timing of these new protocols more into focus. Public information show many vendors moving to the first version of LTE by 2011. Sprint’s very fast WiMax and cell is available in many urban areas today and will hopefully spread fast.
So, brace yourself for the innovation that will drive in the devices that connect to the cloud through cellular.
For more on 4G I recommend wikipedia at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/4G